
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is the inability for an individual to hear sounds as usual.
This often manifests as a difficulty to understand other people due to irregular frequency of sounds. This can be even worse in a rowdy environment where background noise interrupts speech or statements.
The extent of hearing loss varies, from mild all the way to severe hearing loss, where no sound can be heard no matter how loud it is.
The impact of hearing loss can vary. In some cases it can have a significant impact on the quality of life of an individual. In many cases, it can be overwhelming. Some of these impacts and effects include:• Increased risk of developing dementia
- Impact on personal relationships
- Decline in workplace effectiveness, which may affect income.
- Feeling isolated from the rest of the world
If you are concerned that your hearing is not what it once was, you are not alone. One in six people in Australia have hearing loss. With the ageing of Australia’s population, hearing loss is projected to increase to one in every four Australians by 2050.
There is little that can be done to treat hearing loss, however, with the fitting of hearing devices, associated symptoms of hearing loss may be prevented, improving your quality of life.
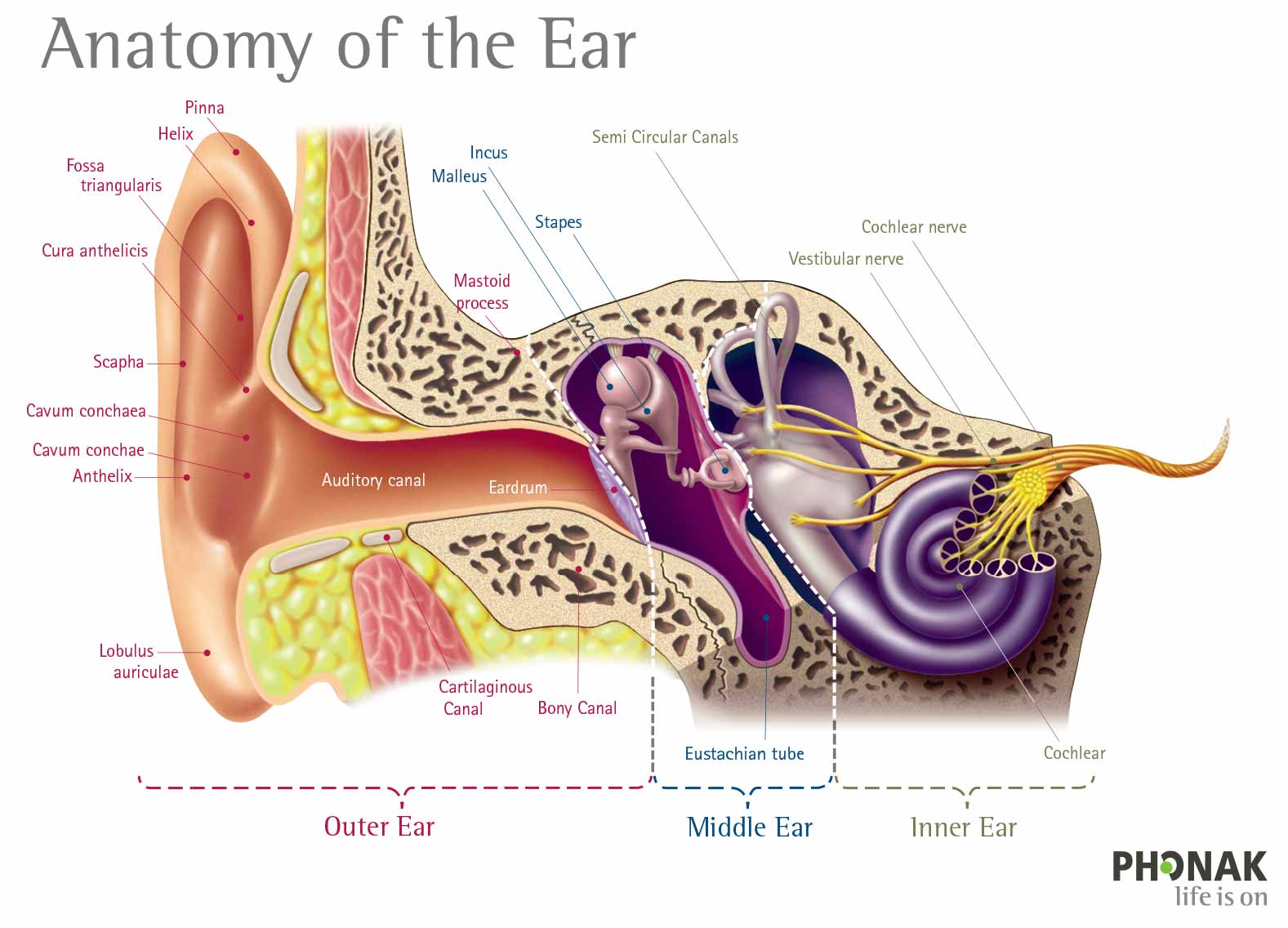
Signs, Causes and Types of Hearing Loss
The three basic types of hearing loss include, conductive, sensorineural and mixed. There is a fourth type of hearing loss that is classified separately because the site of the hearing impairment does not originate from the ear.Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem with the passage of sound through the ear canal to the ear drum, and the ear bones (ossicles).
With conductive hearing loss, the overall volume of sound is reduced, making it hard to hear.
When volume is sufficiently increased, clarity and understanding are usually intact for people with conductive hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss accounts for only 10% of all patients with hearing loss. The exciting news is that this type of hearing loss can be medically or surgically treated, and in some cases, hearing can be totally restored to normal.
Some of the conditions that may result in conductive hearing loss are:
- Middle ear pathology, with fluid behind ear drum. Patient may sense fullness in the ear and have some fluid drainage from the affected area.
- Perforated ear drum.
- Cerumen impaction. Excessive earwax in the ear canal prevents passage of sounds into the ear canal, tympanic membrane, or audiovestibular system.
- Absence or malformation of the outer ear, ear canal or middle ear
Signs of conductive hearing loss may Include:
- Inability to hear silent sounds
- Fluid drainage from the hear
- Asking people to repeat what they say
- Turning up the volume
- Hearing in one ear better than the other
- Feeling of blockage in the ear
- Ear pain
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing condition, affecting more than 90% of patients with hearing issues.
Sensorineural hearing loss manifests when there is damage to the inner ear (cochlea). In layman’s terms, this means “nerve deafness”.
Nerve deafness can occur across different degrees from mild, moderate, to severe. The higher the degree, the higher the chance of the hearing loss leading to dementia.
Patients with this hearing condition may experience a reduction in actual volume and clarity of sounds. This means that although they can hear people speaking, they cannot understand all the words, even when the volume is adequate.
Common causes include:
- Aging
- Excessive noise exposure
- Genetic syndromes (Inherited from parents)
Other causes may include:
- Auditory nerve tumours
- Drugs that are toxic to the auditory system
- Diseases such as meningitis and Meniere’s disease
- Vascular disease
- Kidney disease
- Head Trauma
Each cause can lead to damage to the sensory hair cells or nerves. Once damaged, the hair cells can’t repair themselves nor be medically treated. Therefore, 90% of hearing loss cannot be cured, however, it can be addressed by appropriate hearing aid device fittings.
Signs of sensorineural hearing loss may include:
- Perception of people mumbling or not speaking clearly
- Lack of clarity when listening to speech
- Difficulty hearing in noisy environment
Mixed Hearing Loss
A condition where both sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss occur at the same time is referred to as mixed hearing loss.
This condition implies there are complications in the inner ear, middle ear and/or outer ear.
As mixed hearing loss is a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, symptoms of either or both conditions may also be present.

The Link Between Dementia and Hearing Loss
The memory loss and subsequent social withdrawal experienced from hearing loss may contribute to cognitive decline and the onset of dementia. Withdrawal from social activities often leads to depression and anxiety, known risk factors for dementia. Managing hearing loss may help protect against cognitive decline by keeping the brain actively engaged in everyday life. Research suggests that these positive effects have the potential to delay cognitive decline and the onset of dementia.

